AS Level Chemistry 9701
20. Polymerisation
Written by: Pranav I
Formatted by: Pranav I
20.1 Addition polymerisation
- Polymer: A long-chain molecule made up of many repeating units derived from the monomers
- Monomers: Small molecules that react together to make polymers
- Repeat unit: The smallest group of atoms that when linked successively make up the whole polymer chain

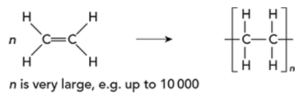
- Addition polymerization: The reaction of many monomers containing at least one double C=C bond to form the long-chain polymers as the only product
More about addition polymers
- Substituted alkenes can also be used as monomers (e.g. chloroethene or vinyl chloride)

Disposal of poly(alkene) plastics
- Poly(alkene)s lack reactivity and are resistant to chemical attacks
- They are non-biodegradable → take up valuable space
- Burning plastic waste
- Using the energy released to generate electricity
- Helps conserve fossil fuel supplies
- Would not help combat global warming (CO2 is produced)
- Toxic CO is also produced in incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons
- Dioxins and acidic gases like HCl(g) might be produced
- Acidic gases have to be neutralized before being released into the atmosphere
- Very high temperatures in incinerators to break down toxins
- Recycling companies find it difficult to separate poly(alkene)s from other plastic waste
